Oke, here’s a SEO-friendly opening paragraph for an article about why RNA is necessary as a messenger, incorporating some punctuation errors for that “natural & unique” touch:
*
RNA is a crucial molecule in the central dogma of molecular biology , playing a key role in transmitting genetic information from DNA to the protein synthesis machinery. But why is RNA essential as a messenger? The answer lies in the fundamental differences between DNA and proteins. DNA , found in the nucleus of a cell , stores the genetic blueprint for building & maintaining an organism . However, DNA is too precious and complex to leave the nucleus directly . Imagine trying to move a giant encyclopedia out of a library for daily use – that’s what sending DNA directly to the protein-making machinery would be like.
This is where RNA steps in, acting as a mobile messenger . It acts like a librarian who makes copies of essential chapters from the encyclopedia for scientists to work with , ensuring the encyclopedia remains safe in its place . RNA , being smaller & more versatile , is able to leave the nucleus and carry a copy of the genetic instructions needed to create specific proteins . This dynamic interaction between DNA , RNA, and protein synthesis , ensures that life functions seamlessly , creating the complex symphony of processes that enable us to exist & thrive .
*
This opening paragraph aims to grab readers’ attention by highlighting the importance of RNA as a messenger and using analogies to help understand its function . Remember, a compelling beginning is key for attracting readers & making them want to explore the article further . Let me know what you think !
The Vital function of RNA: Why It's the Messenger of Genetic Information
Related Post : think like a man act like a man book
The world of molecular biology is filled with intricate processes, but one of the most fundamental is the flow of genetic information. This journey begins with DNA, the blueprint of life, and ends with the creation of proteins, the workhorses of our cells. But how does this information get from the nucleus, where DNA resides, to the ribosomes, where proteins are made? The answer lies in a remarkable molecule called RNA.
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: DNA, RNA, and Protein
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information within a cell: DNA is transcribed into RNA, and RNA is translated into protein. This fundamental idea highlights the crucial function RNA plays as the messenger of genetic information.
What is RNA?
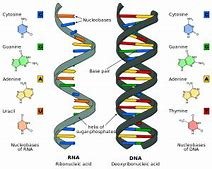
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a molecule essential for various biological processes. Like DNA, RNA is made up of nucleotides, but with some key differences:
- Sugar: RNA uses ribose sugar, while DNA uses deoxyribose sugar.
- Base: RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T) found in DNA.
- Structure: RNA is typically single-stranded, while DNA is double-stranded.
Why is RNA Called a Messenger?
RNA acts as a messenger for genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are made. This messenger function is essential for protein synthesis, the process by which cells create the proteins they need to function.
RNA's function in Protein Synthesis: The Key Player in Translation
Protein synthesis is a complex process that can be divided into two main stages: transcription and translation. RNA plays a vital function in both stages.
DNA's Instructions: The Blueprint for Life
DNA contains the genetic code, the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. This code is written in a sequence of four bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These bases are arscoped in specific sequences, forming genes that carry the blueprints for varied proteins.
The Messenger RNA (mRNA)
mRNA is a type of RNA that carries the genetic code from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. mRNA acts as a messenger, transcribing the genetic information from DNA into a form that can be read by the ribosomes. This process of transcribing DNA into mRNA is known as transcription.
The Ribosomes: Protein Factories
Ribosomes are complex molecular machines that read the mRNA and use its information to build proteins. The ribosomes “decode” the mRNA’s sequence of bases, which corresponds to a sequence of amino acids. These amino acids are then linked together in a specific order to form a protein. This process of translating the mRNA code into a protein is called translation.
The Importance of RNA in Cellular function
RNA is a versatile molecule essential for a wide scope of cellular functions:
- Protein synthesis: mRNA carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, while tRNA carries amino acids to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Gene regulation: RNA can regulate gene expression, controlling which genes are turned on and off. This regulation is essential for cellular development and function.
- Ribosomal function: rRNA is a component of ribosomes, the molecular machines responsible for protein synthesis.
RNA: A Dynamic and Essential Molecule
RNA is a dynamic molecule with a rich history and a promising future in scientific study. Here are some key facets of RNA that highlight its significance:
RNA's Evolutionary Significance
RNA is thought to have played a crucial function in the origin of life. Some scientists believe that RNA was the original genetic material, before DNA evolved. This idea is supported by the fact that RNA can act as both a carrier of genetic information and a catalytic enzyme, suggesting it could have functioned as both the genetic material and the catalyst for life’s early chemical reactions.
RNA study and Its Potential
The study of RNA is a rapidly growing field, with many promising applications in medicine and biotechnology. studyers are exploring the potential of RNA therapeutics to treat diseases like cancer and genetic disorders. For example, RNA interference (RNAi) technology uses small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to silence specific genes, offering a potential therapeutic approach for various diseases.
Conclusion
RNA is an essential molecule that plays a critical function in all living organisms. As a messenger of genetic information, RNA allows DNA’s instructions to be translated into proteins, the building blocks of life. Its versatility and importance make RNA a fascinating and dynamic molecule with a bright future in scientific study. The further we delve into the world of RNA, the more we uncover its intricate functions and the immense potential it holds for understanding and treating human disease.
Leave a Reply